SL: Service Level
Updated: Dec 16, 2025 Reading time ≈ 5 min
SL (Service Level) is a core KPI used in service management and support to describe how reliably and how quickly a provider delivers services to customers.
In practice, SL is usually formalized in Service Level Agreements (SLAs)-contractual commitments between the provider and the client. SLAs can include targets for:
- response time to requests or incidents,
- time to resolution,
- system availability (uptime),
- quality of support and communication.
For example, an SLA might state that 80% of calls must be answered within 20 seconds or that availability must be at least 99.9% per month. SL therefore becomes a measurable bridge between operational performance and Customer Experience outcomes such as CSAT, NPS, or CES 2.0.
Purpose of SL Evaluation
SL evaluation is used to bring structure and accountability to service delivery.
- Defining expectations. Clear SL targets turn vague "good service" promises into concrete, measurable commitments. This reduces misunderstandings and helps both parties align on what "acceptable service" means.
- Measuring performance. SL metrics make it easy to see whether teams are meeting agreed goals-response times, resolution times, uptime, and other operational indicators.
- Improving service quality. Regular SL reviews highlight weak spots in processes or capacity planning. Combined with IQS (Internal Quality Score) or audits, they show where quality is slipping and why.
- Managing customer relationships. Transparent reporting on SL builds trust and supports constructive discussions with clients about priorities, trade-offs, and improvement plans.
- Regulatory and contractual compliance. In some sectors (finance, healthcare, telecom), SLAs and their reporting are part of regulatory requirements. SL data demonstrates compliance.
- Financial and strategic planning. SL performance can be linked to penalties, bonuses, or contract renewals. Over time, SL trends inform strategic planning, capacity investment and process redesign.
How the SL Metric Is Calculated
The exact SL formula depends on the agreed target (calls, tickets, uptime, etc.). A classic example from call centers:

Example
- Target to answer a call: 20 seconds
- Calls answered within 20 seconds: 75
- Total calls that entered the queue: 100
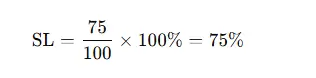
This means 75% of incoming calls met the agreed threshold.
Other SL formulas might track:
- % of incidents resolved within SLA by priority,
- % of tickets first-responded within FRT,
- % of cases solved in a single interaction (FCR),
- uptime over a given period.
SL metrics are often analyzed using time series analysis to monitor trends and seasonality.
General Methodology for SL
Implementing SL as a robust management tool usually involves:
1. Defining indicators. Decide which metrics reflect service level best: response time, resolution time, uptime, backlog, quality or a combination.
2. Setting targets. Establish realistic yet ambitious thresholds based on:
- industry benchmarks,
- historical data,
- customer expectations and contract terms.
3. Building data collection. Configure systems (telephony, ticketing, monitoring tools) to:
- log all interactions and events,
- capture relevant time stamps, statuses, and categories.
4. Calculating and aggregating SL. Calculate SL per interval (hour, day, month) and segment:
- channel (phone, chat, email),
- priority,
- team or region.
5. Analyzing and diagnosing. Use cross-tabulation and quantitative analysis to detect patterns:
- peak hours where SL drops,
- queues or channels with chronic underperformance,
- correlation with quality metrics (CSAT, IQS) or Churn Rate.
6. Communicating and acting. Discuss SL results with teams, management, and key customers; translate insights into staffing changes, process improvements, or SLA updates.
7. Continuous review. SL is part of a PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle: targets and methods should be revisited as products, volumes, and expectations evolve.
What Is Considered a Normal SL Level?
There is no single "correct" SL value-targets depend on industry, service type, and risk tolerance. Still, some patterns are common:
- Call centers and support desks. Targets such as 80/20 or 90/10 are typical:
- 80% of calls answered within 20 seconds, or
- 90% of calls answered within 10 seconds.
- IT support and service operations. Different SLAs by priority:
- critical incidents: response in 15–60 minutes,
- medium priority: a few hours,
- low priority: next business day or longer.
- Online services and applications. Availability is often targeted at 99.0–99.99% ("two, three, or four nines"). Higher uptime generally means higher infrastructure and redundancy costs.
A "normal" SL should be:
- aligned with customer expectations and business value,
- achievable with current or planned resources,
- clearly measurable and auditable.
Companies frequently combine SL performance with outcome metrics like CSAT, NPS, CES 2.0, or Repurchase Rate to see whether meeting SLAs actually translates into better customer outcomes.
How to Improve the SL Metric
Improving SL typically requires both operational and organizational changes:
- Analyze current performance deeply. Identify when and where SL drops-specific queues, shifts, regions, or issue types. Look at SL together with FRT, FCR, TTR, backlog, and quality metrics.
- Right-size and schedule resources. Adjust staffing to demand patterns; use forecasting based on time series analysis. Consider cross-training staff to handle multiple queues.
- Streamline and automate processes. Simplify workflows, remove bottlenecks, and automate repetitive steps with ticket routing, templates and macros.
- Implement smart prioritization. Use clear rules for handling critical vs low-priority requests, ensuring high-impact issues get fast attention without blocking everything else.
- Invest in tools and infrastructure. Modern CRM, omnichannel platforms, monitoring tools, and self-service portals (knowledge base, FAQ, chatbots) can reduce load and response times.
- Train and support teams. Equip agents and engineers with the skills and information needed to resolve issues quickly and accurately-even when volumes spike.
- Improve communication and expectations. Set realistic SLAs, communicate them clearly, and provide proactive updates during outages or peak loads. Clear expectations reduce perceived "service failures" even when SL is under pressure.
Improving SL is not about chasing a single number in isolation. The goal is to maintain a sustainable balance between speed, quality, cost and customer satisfaction-so that service levels support long-term relationships and healthy business growth.
Updated: Dec 16, 2025 Published: Jun 2, 2025








 Mike Taylor
Mike Taylor