CSI: Customer Loyalty Index
Updated: Dec 9, 2025 Reading time ≈ 9 min
CSI (Customer Satisfaction Index) - sometimes also referred to as Customer Loyalty Index - is a quantitative measure of how satisfied customers are with a company's products or services.
CSI is part of the broader customer experience toolkit, alongside metrics like CSAT, CSS, NPS, mNPS, ACSI, NSS, CDSAT, IQS, CDI, and CHS.
Typically, CSI is calculated using customer surveys, where respondents rate different aspects of their experience:
- product quality,
- customer service,
- pricing,
- ease of use,
- perceived value, etc.
Ratings are usually given on a Likert scale (for example, from 1 to 10, where 1 = "very dissatisfied" and 10 = "very satisfied").
For many companies, CSI becomes a core KPI: a single number that summarizes satisfaction across multiple touchpoints and helps track how changes in product, service, or processes affect customers over time.
If you're just starting out, it's easiest to use a ready-made Customer Satisfaction Index survey template in a tool like SurveyNinja, and then adapt the questions to your industry and audience.
What is CSI used for?
CSI is used across business, marketing and custdev to answer a key question: "How well are we meeting customer expectations?"
Here are the main applications.
1. Measuring customer satisfaction at scale
CSI provides a quantitative summary of how well your product or service delivers on what customers expect.
Compared to a single CSAT question, CSI:
- aggregates several dimensions (quality, service, price, usability, etc.),
- supports cross-tabulation (e.g., satisfaction by segment, channel, product),
- and can be used in time series analysis to track trends.
This makes it useful for both operational dashboards and strategic reviews.
2. Identifying areas for improvement
By breaking CSI into sub-scores (e.g., product quality CSI, support CSI, price CSI), you can:
- see which dimension pulls the overall score down,
- perform gap analysis between expectations and actual experience,
- use factor analysis or predictive analysis to find drivers of overall satisfaction.
Combining CSI with qualitative research (open-ended questions, IDI, Focus Groups, ethnographic research) helps you understand why scores look the way they do.
3. Comparing with competitors and benchmarks
CSI can be compared:
- with industry benchmarks such as ACSI,
- with competitor scores (if available),
- or with your own past values (internal benchmarking).
When combined with metrics like Churn Rate, Customer Retention, Repurchase Rate, and LTV, CSI offers context: a higher CSI should generally correlate with stronger loyalty and better economics.
4. Predicting customer behavior
CSI is often used in quantitative research models to predict:
- likelihood of repeat purchase,
- likelihood of churn,
- impact on LTV,
- word-of-mouth and recommendation (alongside NPS, mNPS, eNPS internally).
In more advanced setups, CSI feeds into predictive analysis models together with behavioral data (RFM, web analytics, CPC acquisition data etc.).
5. CRM and VOC programs
CSI is commonly embedded in CRM and VOC (Voice of the Customer) processes:
- customers with very low CSI scores may trigger TTR-monitored follow-ups,
- customers with high CSI and NPS scores can be invited to loyalty or advocacy programs,
- CSI by segment informs targeted Pulse Surveys and panel studies.
It can also be linked with employee engagement surveys and VOE (Voice of the Employee) to explore the link between internal culture and external customer satisfaction.
6. Improving profitability and internal culture
Higher CSI is frequently associated with:
- better retention and yield rate,
- lower cost-to-serve and fewer complaints,
- reduced marketing spend per unit of revenue, since loyal customers return more often.
Internally, regular CSI measurement encourages a customer-centric culture: employees see how their actions affect CSI and related metrics like CSAT, CES, NPS, FCR and FRT.
How is CSI calculated?
CSI is typically calculated from survey data collected across several satisfaction dimensions. The simple version uses an average of scores.
Basic example
Suppose a company measures satisfaction across four aspects:
- Product quality – average rating 8.5
- Customer service – average rating 7.0
- Pricing policy – average rating 7.5
- Ease of use – average rating 8.0
All are rated on a 1–10 Likert-type scale, and the company decides each aspect is equally important.
A simplified CSI:
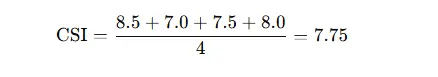
So the overall CSI is 7.75 out of 10.
Weighted CSI and more advanced approaches
In practice, CSI models may:
- assign weights to each dimension (e.g., product quality might matter more than price),
- use Weighted Survey techniques if some groups are over- or underrepresented in the sample,
- incorporate factor analysis or IRT to derive latent satisfaction factors,
- use Z-tests and confidence intervals to compare segments or time periods.
You can do simple averaging in tools like SurveyNinja or export data via API to a BI system for more advanced modeling.
General methodology for CSI surveys
A solid CSI program is not just about the formula - it's about survey design, sampling, and analysis. Here's a typical workflow.
1. Define objectives and scope
Before you start:
- Decide which parts of the customer journey (CJM) you want to cover – onboarding, support, delivery, etc.
- Clarify how CSI will be used – tracking, gap analysis, prioritization, TRI*M style relationship modeling, etc.
- Decide whether you are doing a one-time cross-sectional survey, a longitudinal study or a panel study.
2. Design the questionnaire
A good CSI questionnaire:
- uses clear, specific questions for key dimensions (quality, service, price, usability, value),
- relies on consistent Likert scales or Guttman scales for ordered items,
- includes optional VAS or SUS / SUPR-Q / UMUX / UEQ items for UX-heavy products,
- uses a few open-ended questions for qualitative analysis (e.g., "What's the main reason for your score?").
Before full rollout, it's wise to run a pilot study or do cognitive interviewing to ensure questions are understood as intended.
3. Define target audience and sampling
Your sample should reflect the customer base. To achieve this:
- Use random or stratified sampling instead of pure convenience sampling.
- If you rely on snowball sampling (e.g., in B2B contexts), be explicit about its limitations.
- In panels, monitor panel attrition over time.
When needed, data can be adjusted afterward using weighted survey methods to better reflect the population.
4. Data collection
CSI data can be collected through:
- online surveys (email, in-app, website),
- phone interviews,
- face-to-face or focus groups,
- pulse surveys embedded into existing flows.
Be mindful of the Hawthorne Effect: respondents might temporarily change behavior simply because they know they're being studied. Keep the survey short, clear, and as non-intrusive as possible.
5. Data analysis and CSI calculation
Once data is collected:
- clean it (remove duplicates, obviously invalid responses, validity scale checks if you use them),
- compute averages and sub-indexes,
- analyze differences by segment using cross-tabulation and statistical tests,
- combine ratings with sentiment analysis of open-ended responses.
Then calculate CSI (overall and dimension-level) and track results in SurveyNinja's analytics and reporting or your own BI tool.
6. Interpretation and reporting
Interpret CSI in context:
- compare with past values (trend analysis),
- compare with other satisfaction metrics (CSAT, NPS, CES, CSS),
- relate to behavioral outcomes (retention, churn, repurchase, redemption, LTV).
Summarize key findings in a report that highlights:
- main drivers of satisfaction,
- problem areas,
- impact on business metrics,
- actions and owners.
What is a normal CSI score?
There is no single "normal" CSI value that fits every company. It depends on:
- industry and competition,
- product category (commodity vs premium),
- price segment,
- expectations and culture in the market.
As a rough reference, many organizations consider:
- CSI of 7.5/10 (75%) or higher as a high score,
- scores in the 6.5-7.5 range as "acceptable but with room to improve,"
- scores below 6.5 as a potential warning sign.
Rather than chasing an abstract "perfect" number, it is more useful to:
- compare with industry benchmarks (like ACSI or sector-specific studies),
- monitor trends over time (is CSI rising or falling?),
- compare across segments (product lines, regions, channels),
- relate CSI to Churn Rate, Customer Retention, Repurchase Rate, LTV, Yield Rate, etc.
How to improve the CSI metric
Improving CSI is not a one-time project; it's an ongoing cycle of listening, fixing, and iterating. Key strategies include:
1. Analyze CSI data deeply
Go beyond the single number:
- identify which dimensions pull CSI down (quality, support, price, usability),
- analyze results by segment via cross-tabulation,
- run predictive analysis or factor analysis to find main drivers,
- complement CSI with NPS, CSAT, CES/ CES 2.0, and VOC signals.
Use open-ended responses, IDI or focus groups to understand the "why" behind low scores.
2. Align product or service with expectations
Use custdev, conjoint analysis, MaxDiff, and Kano Model Analysis to:
- understand which attributes matter most,
- adjust the product roadmap,
- avoid overinvesting in features that don't move satisfaction.
Run controlled experimental research with random assignment where possible (A/B testing) to see which changes truly improve CSI.
3. Strengthen customer service and processes
Train employees, define standards, and track metrics like FCR, FRT and TTR.
Combine this with Mystery Shopping, internal employee engagement surveys, and periodic Pulse Surveys to see how internal and external experiences align.
4. Personalize and simplify experiences
Use CRM and automation to:
- personalize communication and offers based on behavior and RFM,
- simplify journeys using CJM and gap analysis,
- target at-risk customers identified by low CSI, NPS, or high churn risk.
UX-wise, you can measure improvement with tools like SUPR-Q, SUS, SEQ, UMUX, UEQ, and VAS.
5. Close the feedback loop and communicate changes
Show customers that their feedback matters:
- acknowledge their input,
- communicate what you changed based on surveys,
- invite them to short follow-up surveys to validate improvements.
When changes are meaningful, this often improves both CSI and NPS over time.
6. Build a customer-centric culture
Make CSI and related metrics visible:
- include them in regular team reviews,
- tie them to realistic, healthy KPIs,
- celebrate improvements and learn from drops without blame.
Combine VOE and VOC programs so that frontline employees have both the motivation and the tools to influence satisfaction.
CSI is a powerful way to compress complex customer perceptions into a single metric - but its real value appears when you connect it with behavioral data, other CX metrics, and deep qualitative insights.
If you want to start or upgrade your CSI program, you can use a CSI / satisfaction survey template, distribute it via multiple channels with SurveyNinja's integrations and automation or track CSI alongside NPS, CSAT, CES, Repurchase Rate and LTV in a single analytics view.
Updated: Dec 9, 2025 Published: Jun 2, 2025








 Mike Taylor
Mike Taylor